The Internet of Things: Connecting Devices, Transforming Industries
Introduction
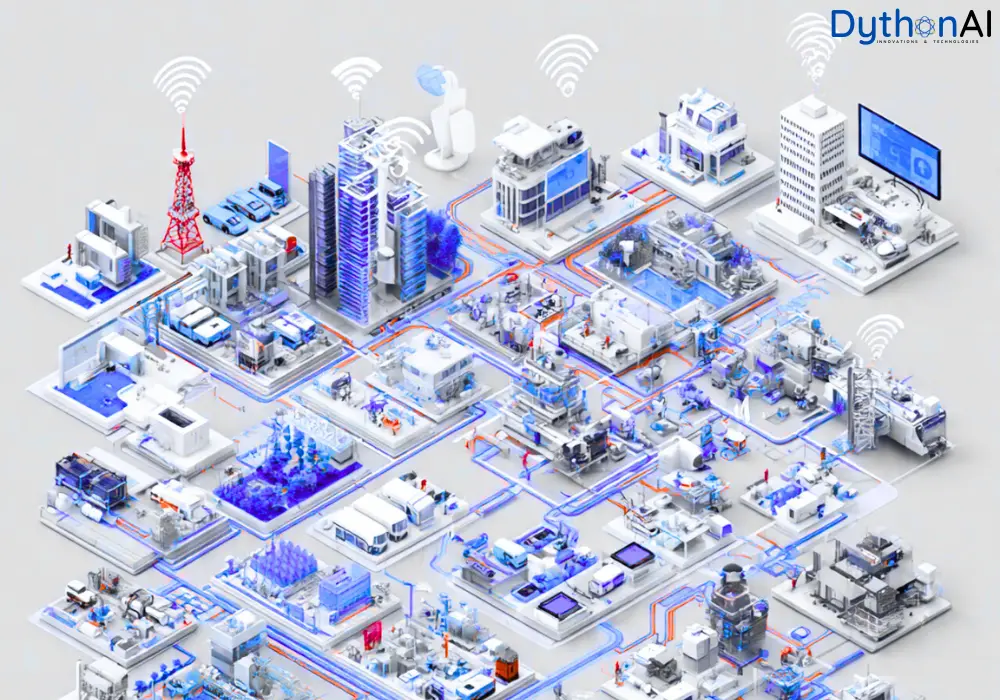
The Internet of Things (IoT) is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s already shaping the way we live, work, and do business. From smart homes and wearable devices to intelligent factories and connected cities, IoT is revolutionizing industries by enabling seamless communication between devices and systems.
At its core, IoT is about connecting physical objects to the internet, allowing them to collect, share, and act on data in real time. This connectivity is unlocking new levels of efficiency, automation, and innovation across the globe.
What Is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things refers to a network of physical devices—such as sensors, machines, vehicles, and appliances—that are embedded with software, sensors, and connectivity. These devices communicate with each other and with centralized systems to analyze data and trigger actions without human intervention.
Examples include:
-
Smart thermostats that adjust temperature automatically
-
Wearable fitness trackers monitoring health metrics
-
Industrial sensors predicting equipment failure
How IoT Works
IoT systems typically follow a simple flow:
-
Devices & Sensors collect data (temperature, motion, location, etc.)
-
Connectivity sends data to cloud platforms via the internet
-
Data Processing analyzes the information using analytics or AI
-
Action is triggered—alerts, automation, or insights
This real-time feedback loop is what makes IoT so powerful.
Transforming Industries with IoT
1. Healthcare
IoT enables remote patient monitoring, smart medical devices, and real-time health tracking. Wearables can monitor heart rate, oxygen levels, and activity, allowing doctors to provide proactive care and reduce hospital visits.
2. Manufacturing
In smart factories, IoT powers predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and improves production efficiency. Machines can detect faults before they occur, saving time and costs.
3. Agriculture
IoT is driving precision farming. Sensors monitor soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health, helping farmers optimize irrigation, reduce waste, and increase yields.
4. Transportation & Logistics
Connected vehicles, GPS tracking, and fleet monitoring improve route optimization, fuel efficiency, and delivery accuracy. IoT also plays a major role in autonomous vehicles.
5. Smart Cities
IoT supports intelligent traffic management, waste management, energy optimization, and public safety. Smart cities use connected infrastructure to improve quality of life and sustainability.
Benefits of IoT
-
Improved Efficiency: Automation reduces manual effort and errors
-
Real-Time Insights: Better decision-making through live data
-
Cost Savings: Predictive maintenance and optimized resource usage
-
Enhanced Customer Experience: Personalized and responsive services
-
Scalability: Easily adaptable across industries and business sizes
Challenges and Security Concerns
Despite its benefits, IoT comes with challenges:
-
Data privacy and security risks
-
Device interoperability issues
-
High initial implementation costs
-
Managing massive volumes of data
Addressing these challenges requires strong cybersecurity practices, secure device authentication, and robust data management strategies.
The Future of IoT
The future of IoT lies in its integration with Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and 5G networks. These technologies will make IoT systems faster, smarter, and more autonomous. As adoption grows, IoT will continue to redefine how industries operate and how people interact with technology.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things is transforming industries by connecting devices, optimizing operations, and enabling smarter decisions. As technology evolves, IoT will play an even greater role in driving innovation, efficiency, and digital transformation across the world.
Businesses that embrace IoT today are positioning themselves for a more connected, intelligent, and competitive future.